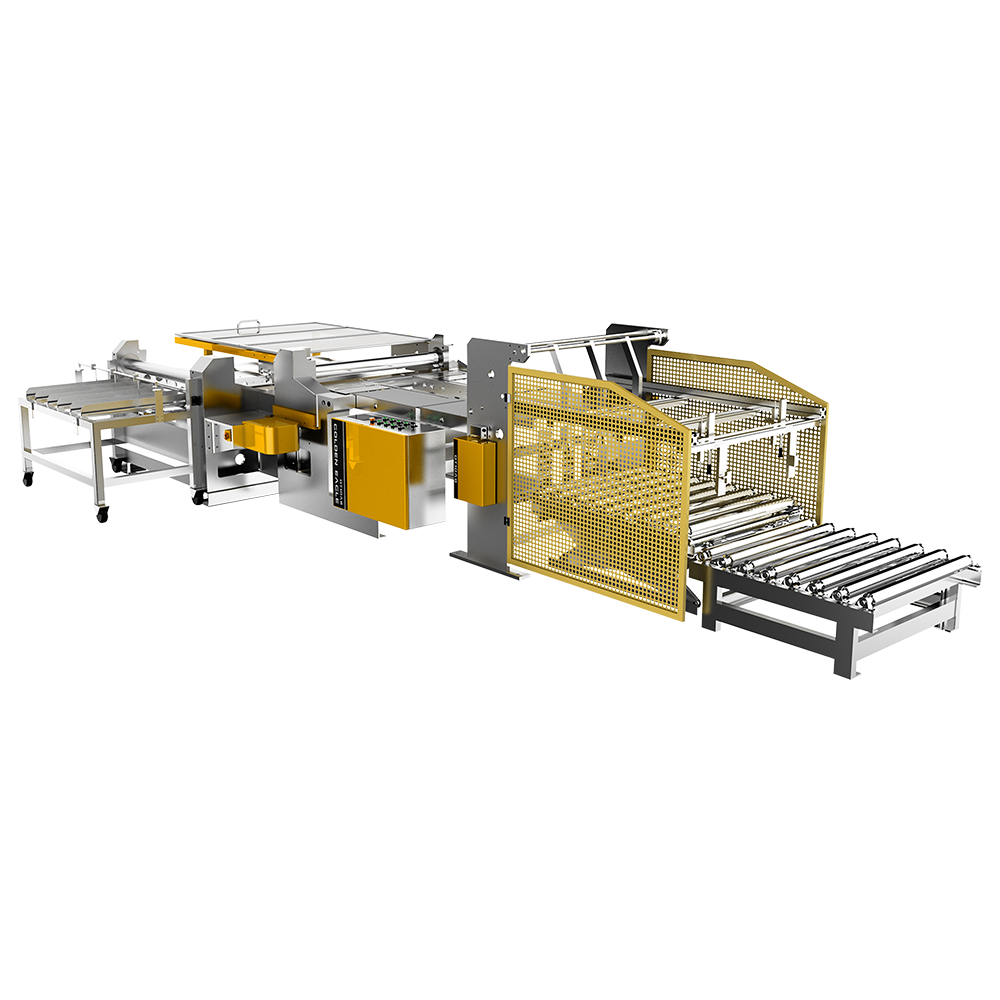
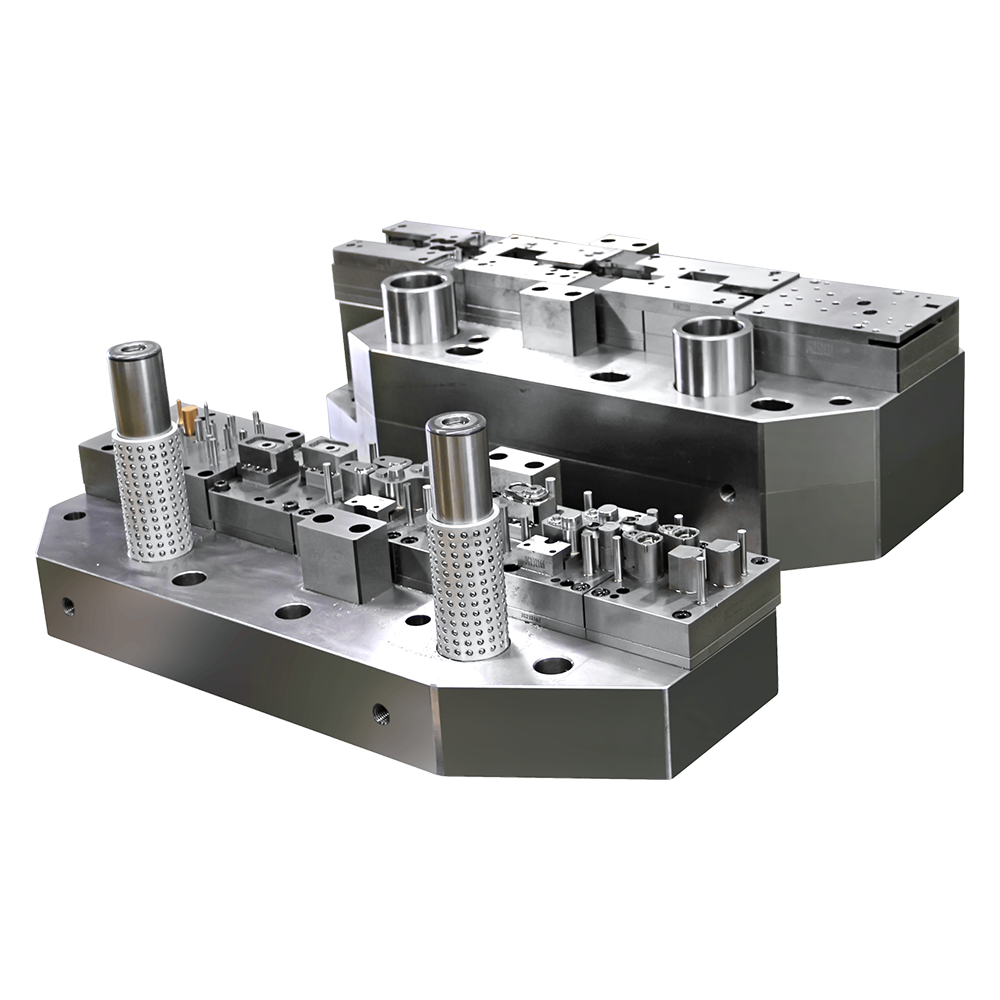
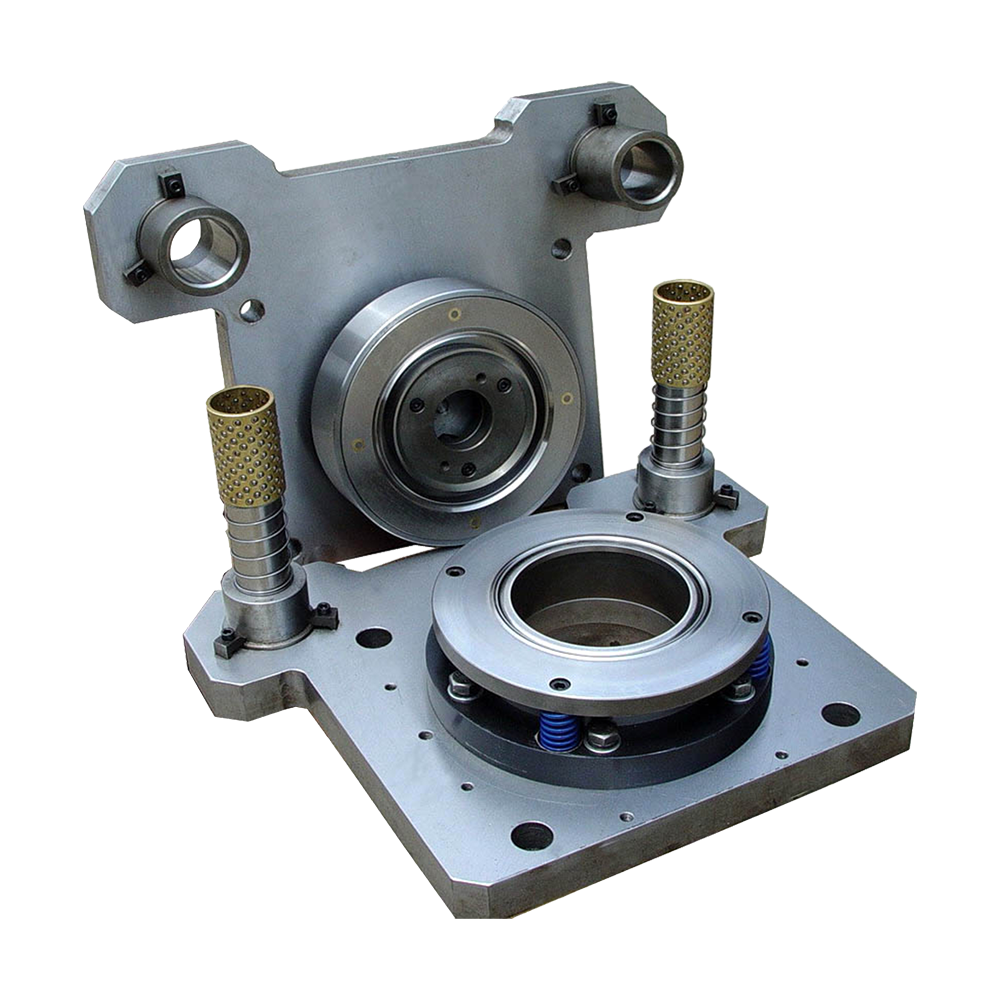
Introduction to Food Beverage Can Making Machines
Food beverage can making machines are essential equipment in the production of aluminum and steel cans for beverages and food products. These machines perform multiple processes including blanking, drawing, ironing, necking, flanging, and sometimes internal and external coating. A common question among manufacturers is whether these machines are suitable for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or large industrial production lines. Evaluating the suitability involves considering production capacity, operational complexity, investment cost, and flexibility in handling different can sizes and materials.
Production Capacity Requirements
The production capacity of a can making machine is a key factor in determining its suitability for different scales of operations. Large industrial production lines typically require machines capable of producing thousands of cans per hour to meet high-volume demand. In contrast, SMEs may need lower capacity machines that can efficiently produce smaller batches while maintaining consistent quality. Modern can making machines offer a range of production capacities, allowing manufacturers to choose equipment that aligns with their production targets, operational hours, and workforce availability.
Machine Size and Footprint
The physical size and footprint of a can making machine also influence its applicability for different enterprises. Industrial-scale machines often occupy significant floor space and may require reinforced foundations, specialized electrical and pneumatic connections, and climate-controlled environments. SMEs, with more limited production space, benefit from compact machines that can deliver reliable output without requiring extensive facility modifications. The availability of modular or smaller-scale machines allows SMEs to implement can production without major infrastructure investments.
Operational Complexity and Skill Requirements
Operational complexity is another important consideration. Large production lines often employ highly automated machines with integrated control systems, sensors, and monitoring software. These machines require skilled operators and maintenance personnel capable of managing sophisticated equipment and troubleshooting complex issues. SMEs may prefer machines with simpler controls, easier maintenance procedures, and lower technical requirements. Choosing the appropriate level of automation ensures efficient operation while matching the skill level of available personnel.
Investment Cost and Return on Investment
Investment cost is a critical factor for both SMEs and large enterprises. Industrial-scale machines involve significant capital expenditure but can achieve high throughput and cost efficiency at large production volumes. SMEs must balance initial investment with expected production output and revenue. Smaller or modular machines provide a lower-cost entry point for SMEs, allowing them to scale operations gradually as demand increases. Understanding the relationship between machine cost, production capacity, and anticipated revenue helps enterprises select equipment that meets financial and operational goals.
Flexibility in Can Size and Material Handling
Different businesses require the ability to produce various can sizes, shapes, and materials. Large production lines often need machines that can handle multiple can specifications without extensive downtime for changeovers. SMEs may focus on a limited range of products and prefer machines that are easy to adjust for different can sizes with minimal technical intervention. Machines that offer flexibility in material handling, such as compatibility with aluminum or steel, as well as the ability to apply internal coatings, benefit enterprises of all scales by supporting product variety and adaptation to market demand.
Maintenance Requirements and Downtime
Maintenance is a key factor affecting suitability. Industrial-scale machines typically have more complex components, including high-speed die sets, multiple drive motors, and advanced lubrication systems, which require routine preventive maintenance and trained technicians. SMEs benefit from machines with simplified maintenance procedures, easily replaceable parts, and accessible service manuals. Minimizing downtime is important for all businesses, but the complexity and frequency of maintenance activities influence whether a particular machine is appropriate for a small, medium, or large-scale operation.
Energy Consumption and Operational Costs
Energy consumption and operational costs must be considered when evaluating machine suitability. Large industrial machines may have higher power requirements but achieve efficiency through high-volume production. SMEs should select machines with lower energy consumption per unit produced to manage operational costs effectively. Evaluating energy efficiency, material usage, and waste reduction features helps enterprises of all sizes optimize overall production costs while ensuring consistent output quality.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Food beverage can making machines are used in a wide range of industries including soft drinks, juices, beer, canned foods, and ready-to-drink products. Large beverage companies rely on industrial-scale machines to maintain continuous production for mass distribution. SMEs, such as craft beverage producers or regional food manufacturers, utilize smaller or modular machines to maintain product quality and flexibility while managing production costs. Case studies indicate that both SMEs and large enterprises can achieve successful outcomes by selecting machines that match production scale and operational requirements.
Advantages of Scalability and Modular Design
Scalability and modular design are advantageous for businesses of all sizes. Modular machines allow SMEs to start with smaller production units and expand capacity as demand grows. Large enterprises benefit from modularity by integrating additional lines or upgrading specific components without replacing the entire machine. The ability to scale production ensures adaptability to market trends, seasonal demand fluctuations, and product innovation, making can making machines suitable for a broad range of business sizes.
Comparison of Can Making Machine Suitability for SMEs vs. Large Industrial Lines
| Factor |
SMEs |
Large Industrial Lines |
| Production Capacity |
Low to medium; suitable for smaller batches |
High; designed for mass production |
| Machine Footprint |
Compact; suitable for limited space |
Large; requires dedicated production facility |
| Operational Complexity |
Moderate; simpler controls and maintenance |
High; automated systems with skilled operators |
| Investment Cost |
Lower; scalable entry point |
High; cost-effective at high volume |
| Flexibility |
Moderate; easy to adjust for few product types |
High; capable of multiple can sizes and materials |
| Maintenance |
Lower complexity; accessible for local technicians |
Higher complexity; requires specialized maintenance |
| Energy Consumption |
Lower per machine; cost-effective for small batches |
Higher total; efficient at large scale |