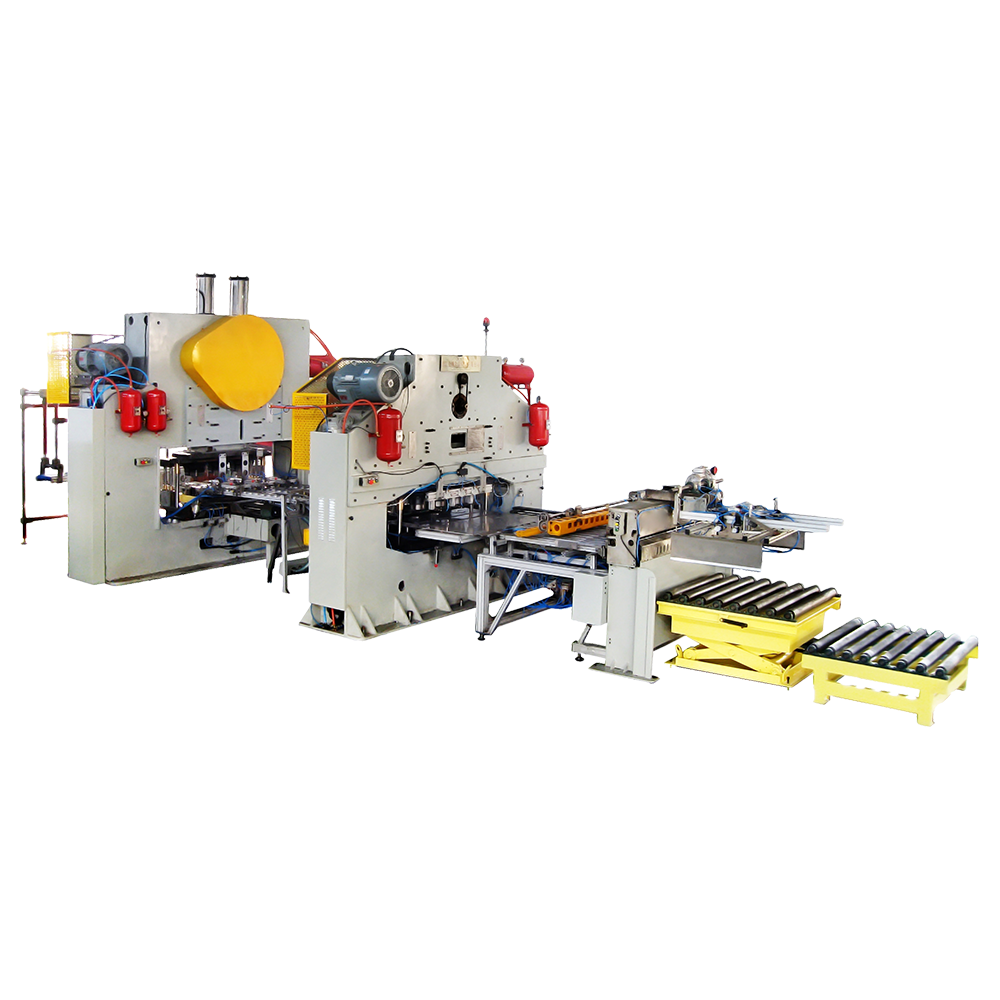
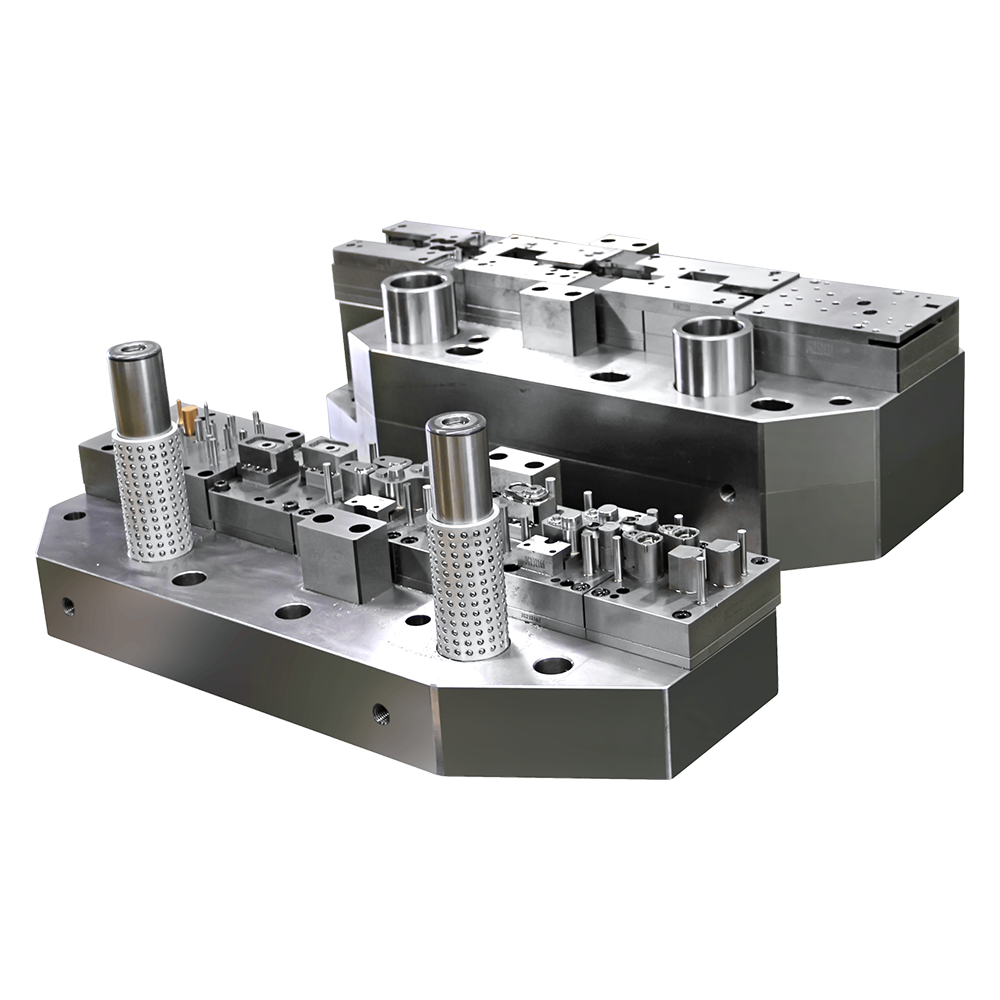
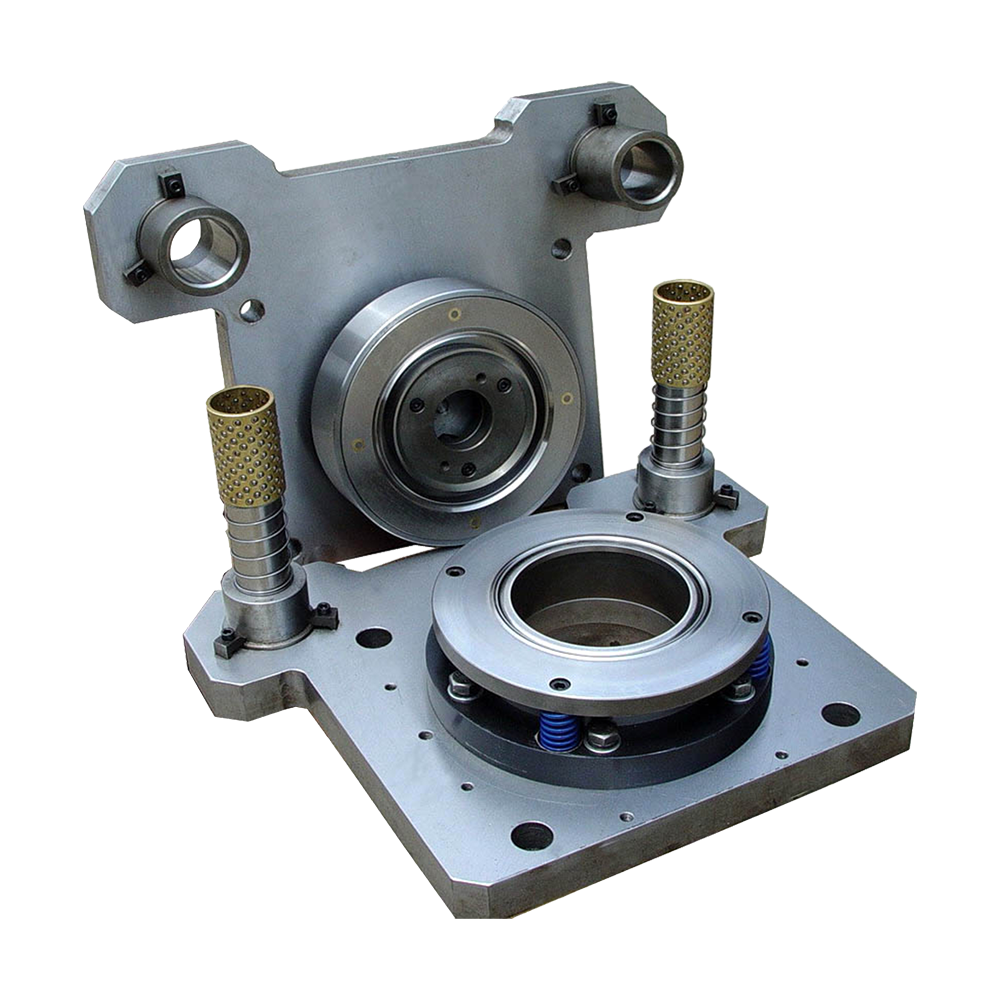
Regularly clean and inspect equipment
Over extended periods of operation, food and beverage can making machines can easily accumulate dust, oil, and metal debris on their internal and external components. If these impurities are not promptly cleaned, they can increase equipment resistance and even cause component wear or failure. Regular cleaning includes thorough cleaning of the transmission components, forming dies, conveyor tracks, and control panel. After cleaning, a careful inspection should be performed to ensure that no parts are loose or damaged. This practice reduces equipment wear caused by dirt and impurities, maintaining stable production efficiency.
Properly schedule equipment operation time
Food and beverage can making machines are high-load machines. Prolonged continuous operation increases component fatigue and accelerates mechanical wear. To extend equipment life, operating time should be strategically scheduled according to production schedules to avoid overload, and appropriate downtime should be scheduled after extended periods of production. A sound operation schedule not only reduces failure rates but also alleviates equipment fatigue, thereby keeping all components in good working condition.
Pay attention to lubrication system maintenance
The lubrication system plays a vital role in reducing friction and wear in food and beverage can making machines. To extend equipment life, it's important to regularly check the quality and quantity of lubricating oil or grease, ensure unobstructed oil passages to lubricated components, and replace them according to the manufacturer's recommended intervals. Insufficient lubrication can lead to excessive wear on mechanical parts, while overlubrication can cause oil accumulation or leakage. Therefore, developing a sound lubrication plan and using lubricants suitable for the equipment are key to maintaining long-term, stable operation.

Regularly Replace Wear Parts
During the production process of food and beverage canning machines, some components, such as molds, seals, drive belts, and bearings, are consumable parts. Their performance gradually deteriorates with age. To prevent cascading failures caused by aging wear parts, a replacement cycle should be established based on equipment operating time and frequency of use, and preventive replacements should be performed before the end of their lifespan. This practice effectively reduces the risk of unplanned downtime and increases the overall service life of the equipment.
Establish Equipment Maintenance Records
Extending equipment life requires not only routine maintenance but also systematic management of maintenance and repair records. Maintaining detailed equipment records, documenting every maintenance, overhaul, and component replacement, helps managers understand the equipment's operating status and identify potential problems promptly. At the same time, by analyzing historical data, maintenance cycles can be optimized and more scientific maintenance plans can be developed, effectively improving equipment efficiency and extending its lifespan.
Strengthening Operator Training
Operator habits directly impact equipment lifespan. Lack of training or improper operation can lead to equipment overload, misoperation, or a lack of necessary daily inspections. Therefore, operators should be provided with systematic training to ensure they master correct operating procedures and daily maintenance techniques. Furthermore, operators should be trained to promptly detect abnormalities during equipment operation, such as unusual noises, vibrations, or decreased production efficiency. Prompt action can prevent problems from escalating.
Improving the Equipment Operating Environment
The operating environment of equipment has a significant impact on its lifespan. Improper control of workshop temperature, humidity, or dust levels can lead to corrosion of equipment components, moisture exposure of electronic components, and increased wear of transmission systems. Therefore, workshops should be kept clean, humidity and temperature controlled within reasonable ranges, and equipment equipped with necessary protective measures, such as dust covers and exhaust systems. A good operating environment not only improves production efficiency but also reduces equipment wear and tear.
Upgrading Technology in Accordance with Production Needs
With the development of the food and beverage industry, manufacturing equipment is constantly being upgraded. To extend the actual service life of equipment, technical modifications or partial upgrades can be used to improve its operating efficiency and stability. For example, adopting new energy-saving motors or more precise control systems can reduce energy consumption and reduce mechanical burdens. Furthermore, technical upgrades can enhance equipment's adaptability, allowing it to continue to operate optimally in response to new production requirements.
Maintenance Items and Cycles for Food and Beverage Can Manufacturing Machines
| Maintenance Item |
Maintenance Content |
Recommended Cycle |
| Cleaning and Inspection |
Clean the surface and internal impurities of the equipment, check fasteners |
Weekly |
| Lubrication Maintenance |
Check lubrication oil lines and refill or replace lubricants |
Monthly |
| Replacement of Wear Parts |
Replace molds, belts, sealing rings, etc. |
Based on usage (3–6 months) |
| System Check |
Inspect control systems and sensors |
Quarterly |
| Comprehensive Overhaul |
Disassemble major components for deep inspection |
Annually |
Major Factors Affecting the Service Life of Food and Beverage Can Manufacturing Machines
| Factor |
Manifestation |
Improvement Measures |
| Improper Operation |
Misoperation, overload operation |
Strengthen training and supervision |
| Environmental Conditions |
Excessive humidity, excessive dust |
Improve workshop ventilation and cleanliness |
| Insufficient Maintenance |
Poor lubrication, untimely repairs |
Establish a scientific maintenance plan |
| Aging of Components |
Wear of molds, belts, and other parts |
Regular replacement of wear parts |