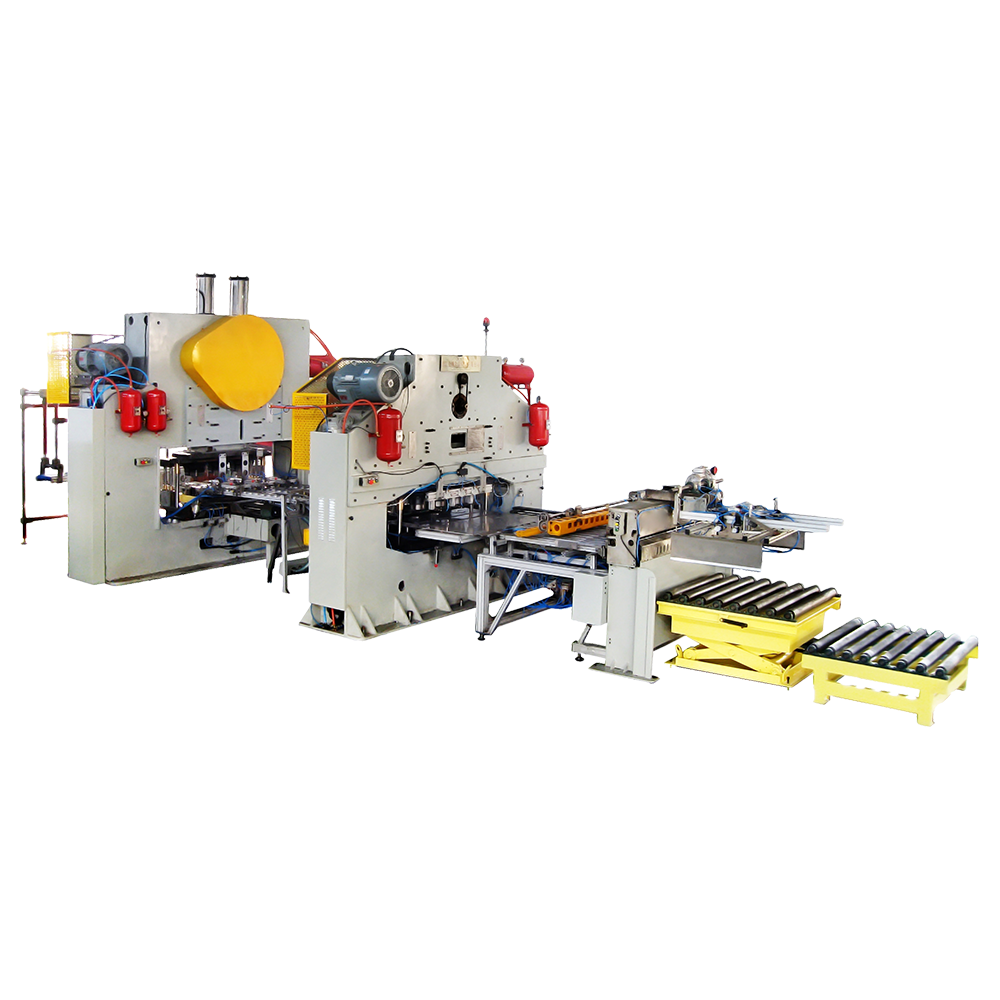
Understanding the Mechanics of Automatic Feeders: Adaptability and Flexibility explores the key aspects that enable automatic feeders to be adaptable and flexible in various industrial applications. Adaptable and flexible feeding systems are essential for accommodating diverse materials, sizes, and production requirements, enhancing efficiency and versatility. This topic could delve into the mechanics behind the adaptability and flexibility of automatic feeders, covering aspects such as
Design Considerations for Adaptability:
Detail the design principles that allow automatic feeders to be easily adjusted or reconfigured. Discuss modular designs, interchangeable components, and customizable features.
Material Compatibility:
Explain how automatic feeders can handle a wide range of materials, from small components to bulk solids. Discuss mechanisms that prevent material clogging or jamming.
Tool-less Adjustments:
Highlight systems that allow operators to make adjustments without the need for specialized tools. This enhances quick setup and changeovers for different materials or production runs.
Feeder Speed and Flow Control:
Explore how automatic feeders can adjust feeding speed and flow rates to match different production requirements. Discuss mechanisms for controlling feed rates and preventing overfeeding.
Size and Shape Adaptation:
Describe how automatic feeders can accommodate materials of varying sizes and shapes. Explain mechanisms like adjustable guides, conveyors, and vibratory trays.
Software and Control Systems:
Discuss the role of software and control systems in enabling adaptability. Touch on programming interfaces that allow operators to input material specifications and feeding parameters.
Changeover Efficiency:
Highlight strategies that minimize downtime during changeovers between different materials. Discuss quick-release mechanisms and user-friendly interfaces.
Sensor Integration:
Explain how sensors and feedback mechanisms contribute to adaptability. Sensors can detect material levels, flow disruptions, and other factors that affect feeding.
Remote Monitoring and Control:
Discuss how remote monitoring and control systems enable adjustments and adaptations from a centralized location. This is particularly useful for maintaining efficiency in dynamic production environments.
Real-world Applications:
Provide examples of industries where adaptability and flexibility are crucial, such as electronics assembly, packaging, pharmaceuticals, and automotive manufacturing.
Benefits of Adaptability:
Highlight the advantages of having an adaptable and flexible feeding system, including reduced changeover times, increased productivity, and minimized material waste.
Training and Operator Skill:
Address the training and skill level required for operators to effectively manage and adjust automatic feeders for different materials and products.
By exploring the mechanics of adaptability and flexibility in automatic feeders, this topic offers valuable insights to professionals involved in process engineering, manufacturing, and automation. It helps them understand how these mechanisms can be optimized to meet the evolving demands of modern production environments.